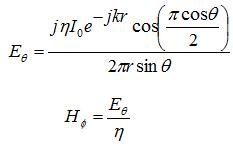天線要能有效率的 radiate, 最好有 common mode signal oscillation, 因為對應的 ground 在無限遠處。 Differential signal oscillation to the first order 會互相抵消,效率會比 common mode signal oscillation 差。 因為 charge 永遠是電中性,只有 differential charge oscillation (如dipole oscillation), 不會有 common mode charge oscillation. Current 則可以有 differential current oscillation (如 small loop) 以及 common mode current oscillation.
Very short dipole antenna 只有 differential charge/voltage oscillation,和 small loop antenna 只有 differential current oscillation 恰好是對偶性 (duality),兩者的效率都很差。如 Table 1.

Table 1: Short dipole antenna and small loop antenna. (Dl = l/4 for half wavelength antenna)
Dipole antenna 利用 dipole 長度增加而產生 common mode current radiation, 如下圖 2. Dipole antenna 最大效率的 common mode radiation 是在長度為 l/2。
長度再更長反而 current 會互相抵消,效率並不會增加。但 radiation pattern 會更集中在一些角度,又稱之為"開花" ,實務上並不常使用。理想的 dipole antenna 是 l/2, 即半波長雙極天線,遠場如下,比 short dipole antenna 公式算出略高,主要是 current distribution 為 sine instead of triangular。或者更常見的,用 l/4 的 monopole 加上 ground plane mirror.
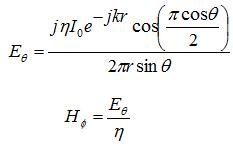
Table 2: Half wavelength dipole antenna.
幾個需要注意的點:
1. monopole 必需是垂直於 ground plane, 而非水平。水平反而會讓 common mode current 變為 differential current, 而抵消 radiation, 變成 small loop antenna. 這也是 RFID 或 Etag 必需要遠離大片金屬的原因,因為 RFID 或 Etag 都是水平貼於表面。
2. 電路產生的 EMI 多半為 common mode noise, 很容易 couple 到 dipole antenna. 最好的解決方法是在 noise source 上做 common mode choke 或 shielding.
3. Dipole antenna 的 differential feed is easy to understand, but how coax feed? or single-ended signal feed?
chart!
如何縮短天線大小
Dipole/monopole 雖然簡單有效,實務上常常遇到的問題是如何縮小天線的尺寸,可以 fit 到機構內。特別對於 sub 1GHz 的 mobile 或 portable 應用 (UHF, GSM-900MHz, ISM-900MHz, LTE-700MHz), 如果有一或兩根突出的天線,不但不美觀,也不安全。如果能 embed 到機構中,更符合美觀和 MIMO 的應用。常用縮短天線的方法:
1. Use monopole instead of dipole: 50% length reduction, refere the previous article for the trade-off between dipole and monopole antenna.
2. Use Meander line structure: The meander-line antenna (MLA) can be in a l/2 dipole or l/4 ground plane format. The idea is to fold the conductors back and forth to make the overall antenna shorter, which is shown in the following figure. It is a smaller area, but the radiation resistance, efficiency and bandwidth decease. The parameters of meander shape will affect the antenna performance parameter. More details about MLA is in the next section.


Meander Line Antenna (MLA)
Meander line antenna is one type of the micro strip antenna. The meander line antenna was proposed by Rashed and Tai for reduce the resonant length. Meandering the patch increases the path over which the surface current flows and that eventually results in lowering of the resonant frequency than the straight wire antenna of same dimensions.
The electrical small antenna defines as the largest dimension of the antenna is no more than one-tenth of a wavelength [5]. Meander antenna is electrically small antenna .The design of meander line antenna is a set of horizontal and vertical lines. Combination of horizontal and vertical lines forms turns. Number of turns increases efficiency increases. In case of meander line if meander spacing is increase resonant frequency decreases. At the same meander separation increase resonant frequency decreases [6]. A meander antenna is an extension of the basic folded antenna and frequencies much lower than resonances of a single element antenna of equal length.
Radiation efficiency of meander line antenna is good as compare to conventional half and quarter wavelength antennas. Antenna size reduction factor β depends primarily on the number of meander elements per wavelength and spacing of element widths of the rectangular loops [7].


Meander line structure to shorten the size; but trade with efficiency
Live antenna vs. dead antenna
Injection power = Ohmic loss + non-radiation mode + radiating mode
where is the power of non-radiating mode? loss again?
why long wavelength has better power in Friss formula
How to deal with Antenna? Any simplified Maxwell equation?
Meander line antenna (MLA) equivalent circuit.